Eczema Treatment: How to Combine Skincare, Lifestyle, and Medical Options
When eczema becomes part of daily life, it often affects more than just the skin. It can influence sleep, mood, work, and social situations. Rather than relying on a single remedy, many people find that combining thoughtful skincare habits, supportive lifestyle choices, and appropriate medical care offers more stable comfort and fewer disruptive flares over time.
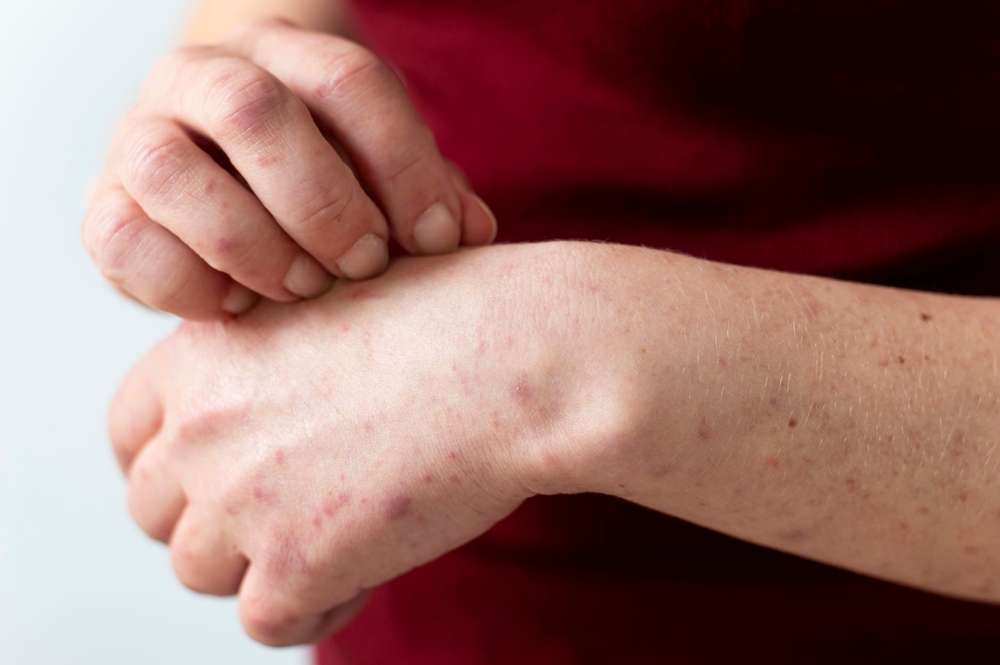
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition marked by dryness, itching, redness, and sometimes small bumps or cracked skin. It often follows a pattern of calm periods and flares, and its intensity can vary from person to person. Because it involves the skin barrier, immune responses, and individual triggers, it usually responds best to a coordinated approach that brings skincare, lifestyle, and medical options together.
Tips for managing eczema effectively
Daily skincare forms the base of most eczema management plans. Gentle cleansing once a day or as recommended, using fragrance-free and soap-free products, helps remove sweat and surface irritants without stripping natural oils. Lukewarm water is usually more comfortable than hot water. After bathing or showering, the skin can be gently patted dry, leaving a little moisture on the surface before applying a rich moisturizer.
Emollients such as ointments and thick creams tend to protect the skin barrier more effectively than light lotions, particularly in dry or cold environments. Applying them at least once or twice a day, and more often during flares, helps reduce dryness and itch. Many people also benefit from identifying personal irritants such as heavily perfumed products, harsh detergents, or rough fabrics and then simplifying their routine to focus on mild, non-irritating options.
Recognizing early signs of a flare is another important tip for managing eczema effectively. Increasing itch, a warm or burning sensation, or small patches of redness may signal that the skin barrier is under stress. Responding quickly by increasing moisturization, avoiding scratching as much as possible, and following any previously agreed medical plan can help limit the extent or duration of a flare.
Guide to combining skincare and medical treatments
For many individuals, emollients alone are not enough to control symptoms, especially during more active phases of eczema. A guide to combining skincare and medical treatments usually begins with preserving the skin barrier through regular moisturization and gentle cleansing, then layering on medical options when needed. Healthcare professionals may prescribe topical anti-inflammatory medicines that are applied directly to affected areas, often for limited periods.
In addition to topical treatments, other medical approaches may be considered for more persistent or widespread eczema. Wet-wrap dressings, where moisturizers and sometimes medications are applied and then covered with damp and dry layers, can increase hydration and help calm intense flares under professional guidance. Light-based therapies and systemic treatments that influence the immune system are sometimes used in moderate to severe cases when simpler measures are not sufficient.
Coordination with a qualified healthcare professional is central when combining different options. Keeping a simple record of flares, products used, environmental conditions, and any suspected triggers may help during consultations. This allows treatment plans to be adjusted over time, including when to use stronger medicines, when to taper them, and how to rotate products to balance effectiveness and safety.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
How lifestyle changes can support healthy skin
Beyond products and prescriptions, how lifestyle changes can support healthy skin is an important part of long-term eczema care. Many people notice that stress, emotional strain, or lack of sleep make itching and irritation feel worse. Techniques such as breathing exercises, relaxation routines, meditation, or gentle yoga may help some individuals manage stress more comfortably, which can indirectly support the skin.
Clothing and environment also influence symptoms. Soft, breathable fabrics such as cotton often feel more comfortable than rough or tight materials. Washing new clothes before wearing them and using fragrance-free, mild detergents can reduce exposure to potential irritants. At home, maintaining a moderate, stable temperature and avoiding very hot baths, saunas, or sudden temperature changes may reduce some triggers. In dry indoor air, a well-maintained humidifier can help prevent additional skin dryness.
Daily habits around exercise and hygiene can be adjusted to support the skin as well. Physical activity can be beneficial for overall health, but sweat and heat may briefly worsen itch. Taking breaks to cool down, showering soon after sweating, and reapplying moisturizer can make exercise more manageable. Nail care and protective measures, such as keeping nails short and considering cotton gloves at night if scratching during sleep is a problem, may help protect the skin from injury.
Food and drink are frequent questions in eczema, but the relationship varies widely. Some people live with both eczema and confirmed food allergies, while many others do not. Removing large groups of foods without medical advice may not improve symptoms and can lead to nutritional shortages. A balanced way of eating that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sources of healthy fats supports general wellbeing. When certain foods appear to consistently coincide with flares, discussing this pattern with a healthcare professional allows for safe evaluation and, if appropriate, supervised testing.
Bringing skincare, lifestyle, and medical care together creates a broader framework for living with eczema. Regular moisturization and gentle cleansing help maintain the skin barrier, targeted medical treatments manage inflammation and intense symptoms, and thoughtful daily habits reduce preventable triggers. Over time, many people come to understand their own patterns, recognize early warning signs, and work with healthcare professionals to adapt their routines, leading to more predictable skin comfort and fewer interruptions to everyday life.




